Read more from Virginia Energy Sense at
https://www.virginiaenergysense.org/
Virginia‘s Energy Plan
Virginia’s energy strategy follows an “all of the above” approach that uses nuclear, natural gas, renewable, and new energy sources to fulfill the Commonwealth’s energy needs.
The Commonwealth’s 2022 Energy Plan recognizes the following five principles as part of ensuring energy access for all Virginians:
- Reliability. Ensure that Virginians have access to energy when and where they need it by preserving the reliability of Virginia’s electric grid.
- Affordability. Keep energy affordable and protect Virginians from rising energy prices.
- Innovation. Bring the Commonwealth to the forefront of energy innovation by embracing and incorporating new renewable energy technologies.
- Competition. Provide Virginians with more choices in where their energy comes from.
- Environmental stewardship. Improve the quality of Virginia’s environment and protect the Commonwealth’s natural resources.
Where Your Power Comes From
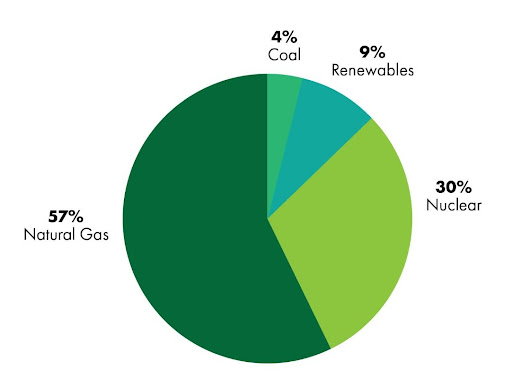
Do you know where your electricity comes from? In Virginia, electricity is generated from a variety of energy sources, including nuclear, coal, natural gas, hydroelectric, renewable, petroleum, and other sources. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, most of Virginia’s electricity is generated from natural gas (57%), nuclear (30%), and renewable (9%) sources. The remainder (4%) comes from coal.
Where Virginians Use the Most Energy
- Heating and cooling. This typically constitutes the largest share of energy usage in homes and workplaces.
- Appliances. Refrigerators, dishwashers, and dryers together account for about 20% of all energy used in homes.
- Water heating. This accounts for about 20% of home energy usage.
- Lighting. Lighting represents the largest share of energy usage in the commercial sector and approximately 15% of the average home’s electricity usage.
- Electronics. Demand in this area is increasing because of advanced computer equipment, more sophisticated televisions and streaming devices, and more.
Virginia’s transportation sector consumes the most energy in the state (30.5% of total usage), followed by the commercial sector (26.8%), residential sector (24.2%), and industrial sector (18.5%).
For more information on the Commonwealth’s energy consumption, see the Energy Information Administration’s Virginia profile.
Demand Response Programs
Rising peak demand can strain the electricity system and potentially hurt the power grid’s reliability. Some energy providers have implemented demand response programs, which give commercial and residential